Accenture is a professional services firm focused on IT consulting and services. Its services are available on a broad global basis, with very few geographies not represented by the company. This company is based in Ireland.
They help clients build their digital business, transform their operations, and aim to accelerate revenue and profit growth. Essentially, Accenture is telling the company that “we can help you do what you do best.”
This is also confirmed by client retention, where 98% of the company’s top 100 clients have been with Accenture for more than 10 years. “Our revenue is derived primarily from Forbes Global 2000 companies, governments and government agencies.” Some of these companies are Adobe, Alibaba, AWS, Salesforce…
The company helps clients in the markets of:
It should be noted that almost 50%-50% of its sales are divided into consulting services and outsourcing services. Most of the consultancy contracts are of short duration (12 months or less) since they deal with finite and determined projects, while outsourcing contracts do have a longer duration. These outsourced services help clients transition to cloud and managed security services and are typically a more iterative and recurring service than consulting.
Accenture helps clients use technology to drive transformation. This includes moving to the cloud, scaling data, artificial intelligence, and built-in security for growth.
Sales segmentation
Its sales are well diversified with almost 50% in the US, but it makes sense as that is where most of the world’s biggest companies are based.
Europe is the segment that grows the least. A.M
Market
Using operations intelligence, enabled by SynOps, the human-machine platform powered by data and analytics, artificial intelligence, digital technology, and exceptional people, it helps businesses achieve their goals of serving customers.
They have managed to increase sales in all groups during the last year (The number in parentheses is the percentage it represents over sales).
Work with US federal government clients is conducted through Accenture Federal Services, a US company and a wholly owned subsidiary of Accenture LLP, and represents approximately 32% of the revenues of the Health and Safety industry. Utilities and 13% of its revenue in North America.
Four major service segments
Technology also includes innovation and R&D activities in the labs and investments in emerging technologies through Accenture Ventures (partners and invests in growth-stage companies creating innovative business technologies)
Competitive advantages
Accenture has several competitive advantages that make it one of the best companies in the world:
Competitors
Accenture is in a sector that is highly competitive by small firms dedicated to IT services, but above all by the well-known “Big Three” McKinsey & Co., Boston Consulting Group, Inc., and Bain & Co.
Being private companies, we cannot compare their figures with those of Accenture, which makes it difficult and increases uncertainty if we speak in terms of competition.
Acquisitions
“Our disciplined acquisition strategy, which is an engine to drive organic growth, is focused on scaling our business in high-growth areas; add skills and abilities in new areas; and deepening our industrial and functional experience.”
In fiscal 2021, they invested $4.2B (compared to $1.5B in 2020 and $1.2B in 2019) in 46 strategic acquisitions, $1.1B in IR&D and $900 million in learning and professional development.
“As of August 31, 2021, we had a portfolio of more than 8,200 patents and pending patent applications worldwide”
In the Conference Call they were asked about the possible absorption problems of all these new M&As and they answered that most of the new acquisitions operate in 1 or 2 markets, some of them very local, so integration is not that difficult, since that you don’t have thousands of people operating all over the world, like you do when you make larger acquisitions.
Management
The CEO is Julie Sweet and she has been since September 2019, although she has been with the company for more than 8 years.
Members of the Board of Directors receive a cash advance and a convertible stock advance of up to $220,000 in addition to the bonuses shown below, with a maximum annual salary of $750,000. In addition, they have to have a stock value 3 times higher than their salary.
General and administrative costs represent 6.83% of sales, which is somewhat high. For the past year, insiders have only sold, but all but the last one were planned sales. On November 2, Julie Sweet (CEO) sold her 11.5% stake in the company through a planned sale.
Capital management has been very good. They have achieved steadily growing EPS and dividends, a reasonable payout, a decrease in shares outstanding (although only 1%) and a good acquisition policy, although this has caused the ROIC of the company to fall, we will see later.
There is still more than $6.6B available for share repurchase (almost 3% of the market cap) or dividend distribution and they hope to distribute it this year, although there are more than 16 million shares available to distribute in the form of stock options. They have been available since 2010.
Returns and margins
ROE and ROIC have almost always been the same and very high. That large ROE has more merit because the company is not leveraged. Even so, it has been declining in recent years. This may be due to acquisitions, but also due to the larger size of the company. In any case, the ROIC is still double the market average.
The growths here are once again higher than the CAGR of sales, highlighting the FCF with a CAGR of 13.45%, due to the previously mentioned reasons.
FCF is almost always higher than profit and it’s all because of accounting, so I would look much more at this metric than net profit.
They have a fairly good and stable EBITDA to FCF conversion rate of 54%.
Accenture’s track record in this section is not bad, but it’s not incredible either. We can see a CAGR on sales of 7.21% and on EPS of 9.80%, thanks to operating leverage and share buybacks. Estimates suggest that it will continue on this path, but in order to be more conservative, I have decided to put that both will increase at a rate of 10% per year. The company says that this increase in sales is not only due to an increase in demand in the sector, but also to all the investments they make to improve and develop new parts of the company.
I have projected profits with an operating margin of 15% and a tax rate of 23%.
The company does not comment on its organic growth, but if we read the conference call, by 2022 they expect growth of 5% inorganic, out of a total growth in sales of 12%-15%, so we can make an approximation of how much Accenture grows organically.
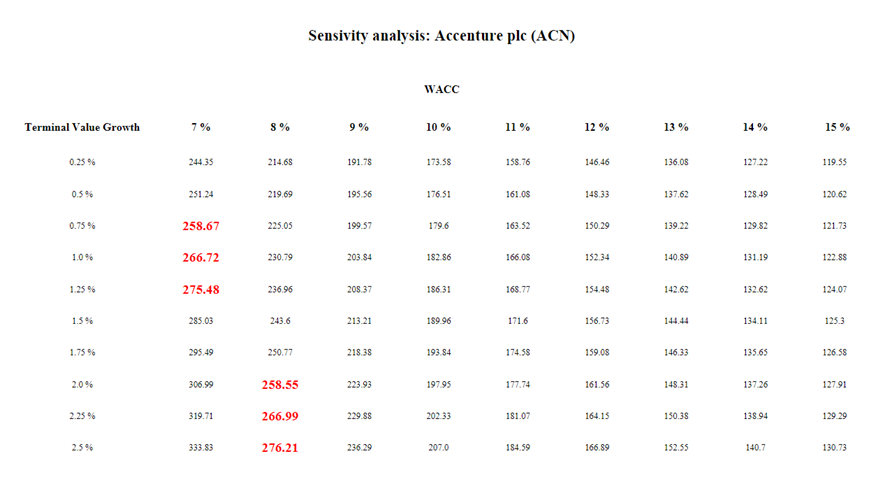
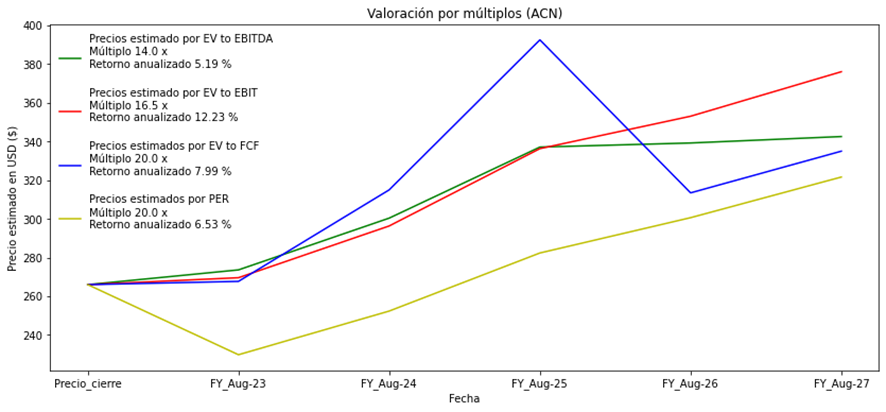
Valuation
Pricing this company against growth expectations results in a 2026 target price of approximately $390, implying an annualized rate of return of 8.3 % (target entry price $260 – $290) over the next 3 years.